CROWNS AND BRIDGES
- Both crowns and bridges are fixed prosthetic devices.A crown or cap is a dental restoration that covers the exposed surface of a tooth to strengthen it or improve its appearance.
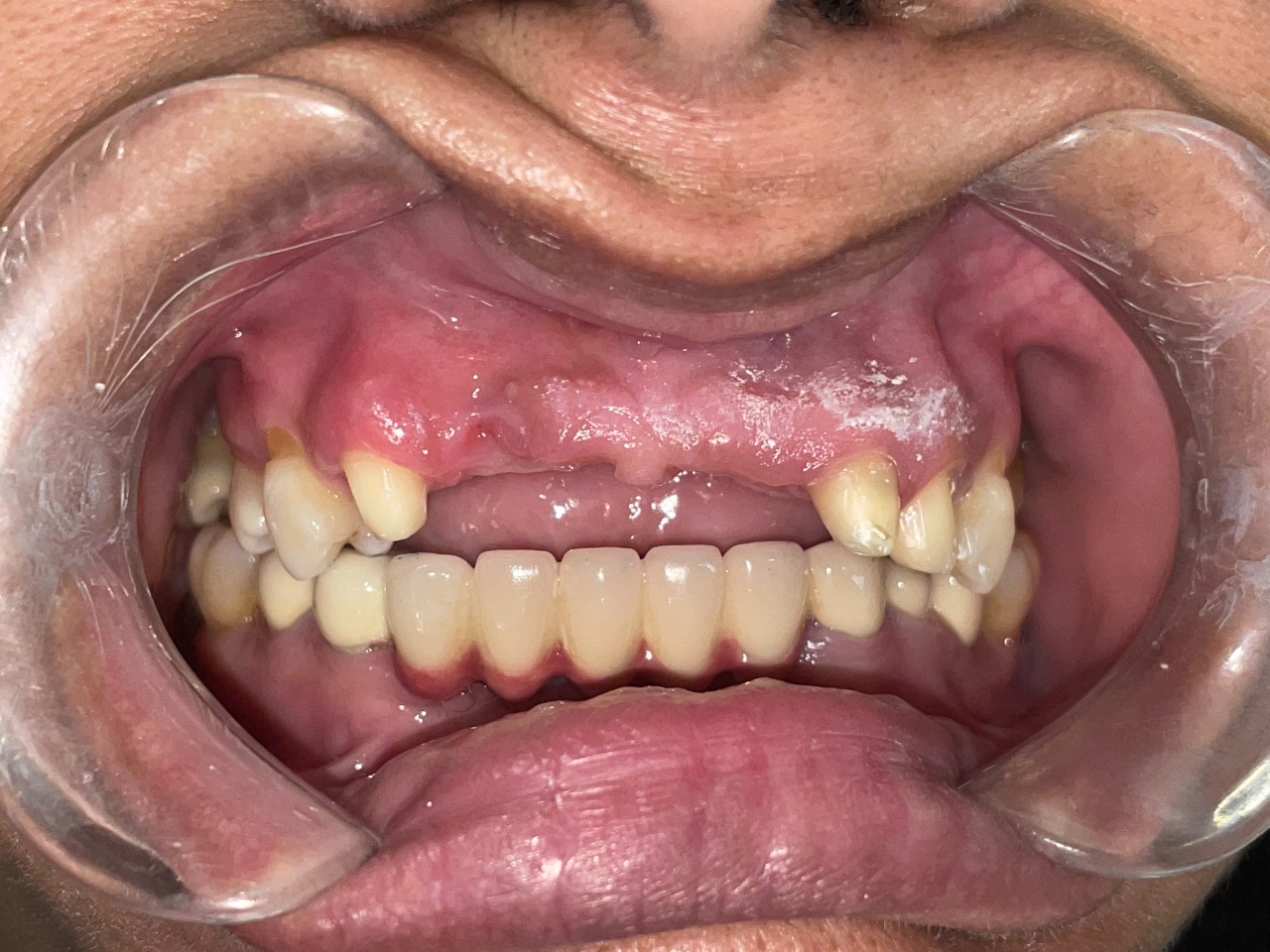
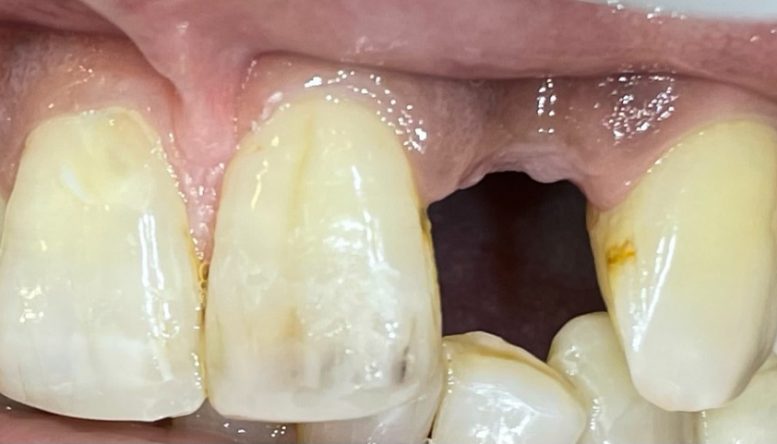
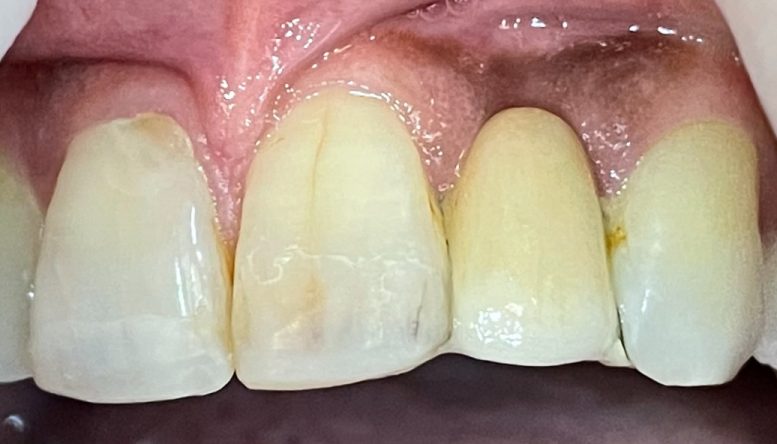
- A bridge is a dental restoration to replace one or more missing teeth. It includes an artificial tooth or teeth which are fused to crowns on either side to provide support.
- Unlike removable devices such as dentures, which you can take out and clean daily, crowns and bridges are cemented onto existing teeth or implants, and can only be removed by a dentist.
– A crown is used to entirely cover or “cap” a damaged tooth. Besides strengthening a damaged tooth, a crown can be used to improve its appearance, shape or alignment.
– A crown can also be placed on top of an implant to provide a tooth-like shape and structure for function.
– Crowns are advised to
- Replace a large filling when there isn’t enough tooth remaining
- Protect a weak tooth from fracturing
- Restore a fractured tooth
- Attach a bridge
- Cover a dental implant
- Cover a discoloured or poorly shaped tooth
- Cover a tooth that has had root canal treatment
- A bridge may be recommended if you’re missing one or more teeth.
- Gaps left by missing teeth eventually cause the remaining teeth to rotate or shift into the empty spaces, resulting in a bad bite.
- The imbalance caused by missing teeth can also lead to gum disease and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
- Bridges are cemented to the natural teeth or implants surrounding the empty space. These teeth, called abutments, serve as anchors for the bridge.
- A replacement tooth, called a pontic, is attached to the crowns that cover the abutments.
– There are various types of materials for fabricating crowns and bridges. Selecting the type of material depends on the factors like clinical condition of the abutment tooth, function, gender (males have higher masticatory forces as compared to females),aesthetics and cost.
– Various materials which are available are
- Metal crowns
- Porcelain fused to metal crowns
- Porcelain/ ceramic facing fused to metal crowns
- Full Porcelain/ceramic crowns
- Zirconia crowns
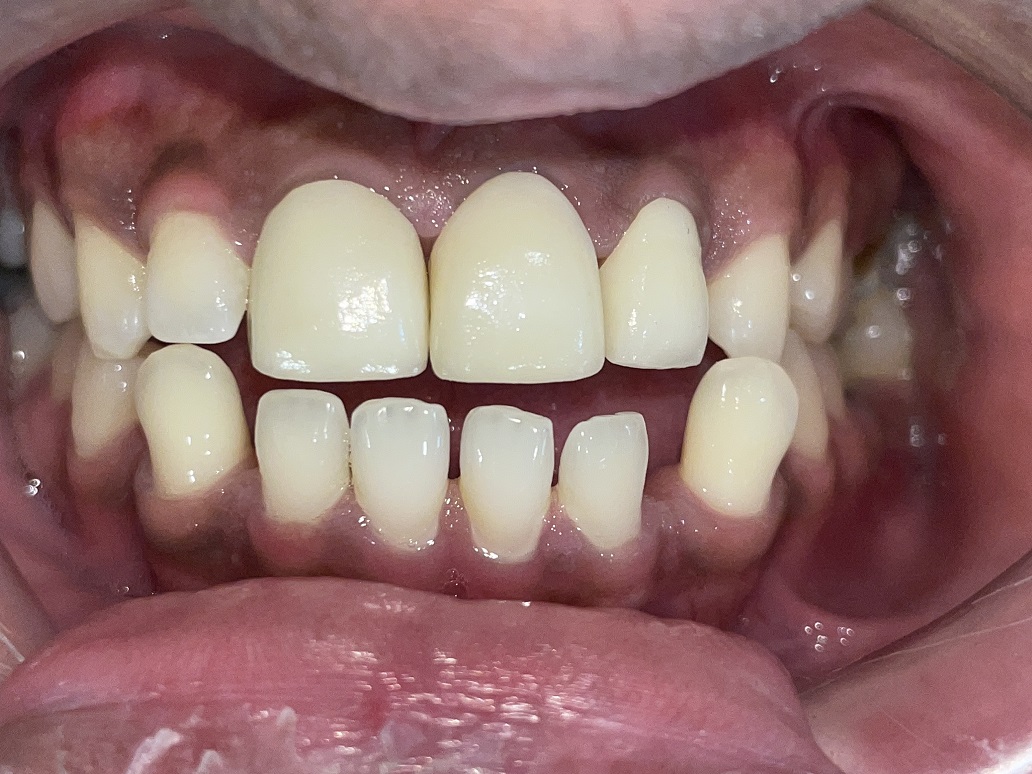
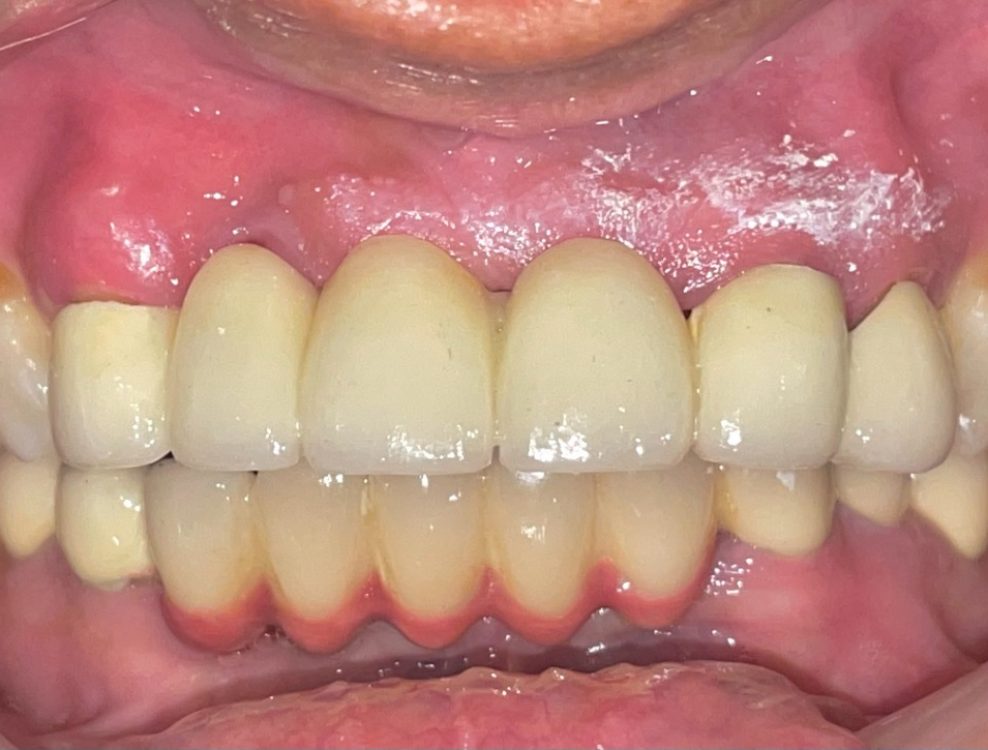
– Porcelain or ceramic crowns can be matched to the colour of your natural teeth.
– Other materials include gold and metal alloys, acrylic, and ceramic. These alloys are generally stronger than porcelain and may be recommended for back teeth.
– Porcelain fused to metal is often used because it is both a strong material and attractive in its appearance.
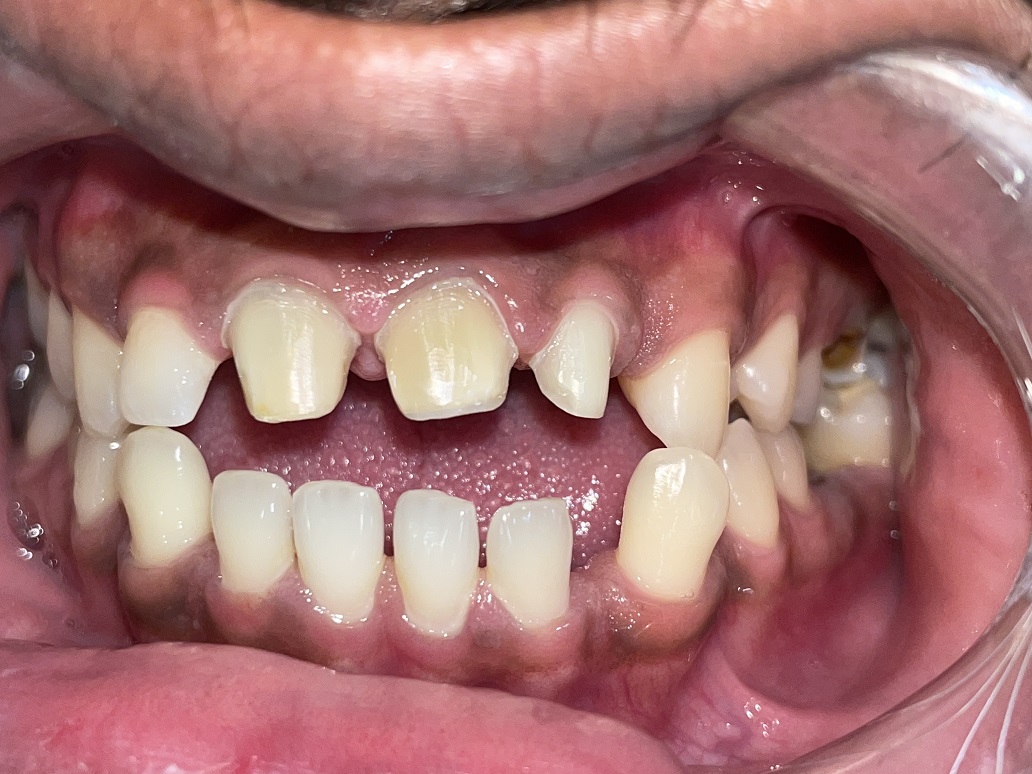
– Before fabricating the crowns and bridges in the lab, dentist/prosthodontist will reduced the size of the tooth according to the material selected for crowns.
– After reducing the tooth, the dentist/Prosthodontist will make an impression of the reduced tooth for making of the working models.
– Also, a temporary/provisional crown/bridge is given to protect the reduced tooth.
– The crown/bridge is fabricated in the lab and cemented by the dentist after checking the extensions and coverage of the crowns.
– While crowns and bridges can last a lifetime, they do sometimes come loose or fall out.
– The most important step you can take to ensure the longevity of your crown or bridge is to practice good oral hygiene.
– Keep your gums and teeth healthy by Brushing with fluoride toothpaste twice a day and flossing daily. Also see your dentist and hygienist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings.
– To prevent damage to your new crown or bridge, avoid chewing hard foods, ice or other hard objects
DENTURES
A denture is a removable replacement for missing teeth and surrounding tissues.
Types:
COMPLETE DENTURE
They can be of two types – CONVENTIONAL and IMMEDIATE
- Conventional denture
- It is made after the teeth have been removed and the gum tissue has begun to heal.
- A conventional denture is ready for placement in the mouth about 8 to 12 weeks after the teeth have been removed.
- IMMEDIATE DENTURE
- Unlike conventional dentures, immediate dentures are made in advance and can be positioned as soon as the teeth are removed.
- As a result, the wearer does not have to be without teeth during the healing period.
- However, bones and gums shrink over time, especially during the healing period following tooth removal. Therefore, it requires more adjustments to fit properly during the healing process and generally should only be considered a temporary solution until conventional dentures can be made.
PARTIAL DENTURE
Types – Resin Partial denture and Cast Partial Denture
- Yes, dental implants can be used to support cemented bridges, eliminating the need for a denture.
- The cost is usually greater, but the implants and bridges more closely resemble the feel of real teeth.
- Dental implants may also be used to support dentures, offering more stability.
- The denture development process takes a few weeks and several appointments.
- Once your dentist or prostho dontist (a dentist who specializes in the restoration and replacement of teeth) determines what type of appliance is best for you.
- The general steps arE:
- Make a series of impressions of your jaw and take measurements of how your jaws relate to one another and how much space is between them.
- Create models, wax forms, and/or plastic patterns in the exact shape and position of the denture to be made. You will “try in” this model several times and the denture will be assessed for colour, shape, and fit before the final denture is cast.
- Cast a final denture.
- Adjustments will be made as necessary.
- New dentures may feel a little odd or loose for a few weeks until the muscles of the cheeks and tongue learn to keep them in place and you get comfortable inserting and removing them.
- Also, it is not unusual for minor irritation or soreness to occur.
- Saliva flow increases when you first start wearing dentures, but these problems will diminish as the mouth
Dentures are made to closely resemble your natural teeth so there should be only a small noticeable change in appearance. In fact, dentures may even improve your smile and fill out your facial appearance.
- Eating with new dentures will take a little practice and may be uncomfortable for some wearers for a few weeks.
- To get used to the new denture, start with soft foods cut into small pieces. Chewslowly using both sides of your mouth. As the patient gets used to new dentures, other foods can be added until patient returns to a normal diet.
- Caution while having hot or hard foods and sharp-edged bones or shells should be followed.
- Avoid foods that are extremely sticky or hard, chewing gum while wearing the denture.
- Also, toothpicks are avoided while wearing dentures.
- After getting dentures, difficulty in pronouncing certain words can be seen. If so, practice by saying the difficult words out loud. With practice and with time patient will become accustomed to speaking properly with dentures.
- If dentures “click” while you’re talking, contact your dentist.
- Dentures may occasionally slip when you laugh, cough, or smile. Reposition the dentures by gently biting down and swallowing.
- If any speaking problem persists, consult your dentist or prosthodontist.
Your dentist or prosthodontist will instruct you as to how long to wear dentures and when to remove them.
A denture adhesive may be considered under the following circumstances:
- To enhance satisfaction with a properly constructed denture. Adhesives enhance retention, stability, bite force, and an individual’s sense of security.
- To assist individuals with dry mouth conditions that lessen denture adherence, such as individuals taking cold medications, those with neurological disabilities including strokes, and the elderly.
- To provide added stability and security for those who place unusual demands on facial muscles, such as public speakers or musicians.
There are situations when denture adhesives should not be used. Those cases include:
- When it is used as a “fix” for ill-fitting or poorly constructed dentures.
- When a dentist has not evaluated dentures for a long time.
- When oral hygiene practices cannot be sustained.
- When adhesives have been used for a long time, especially when visits to the dentist are infrequent, and when the frequency and volume of the adhesive use increases. These developments may indicate the need for a denture adjustment or new dentures.
- When any known allergy exists to the adhesive’s ingredients.
Here are some tips to consider when applying denture adhesives:
- Use the minimum amount necessary to provide the maximum benefit. Apply less than you think you need, and then gradually increase the amount until you feel comfortable.
- Distribute the adhesive evenly on the tissue bearing surface of the denture.
- Apply or reapply when necessary to provide the desired effect.
- Always apply the adhesive to a thoroughly clean denture.
- Remember adhesives work best with a well-fitting denture
- Paste type
- Powder type
- Dental adhesives are safe as long as they are used as directed.
- If the denture is well-fitting and the adhesive is only used to give added stability, there should be no ill effects.
- If adhesives are used excessively to fill voids for an ill-fitting denture, they can be harmful to the underlying soft and hard tissues. Occasionally, in these cases, inflammation of the soft tissues can result.
- In addition, because of its movement on the soft tissue and underlying bone, an ill-fitting denture can cause bone loss.
Caring for Dentures
Proper denture care is important for both the health of your dentures and your mouth.
Here are some tips:
- Handle dentures with great care
- Brush and rinse dentures daily, but not with toothpaste. Toothpaste is abrasive and makes microscopic scratches where food and plaque can build up.
- Use a brush with soft bristles that is designed for cleaning dentures.
- Gently brush all surfaces of the denture, and be careful not to damage the plastic or bend attachments.
- In between brushings, rinse dentures after every meal.
- Clean with a denture cleaner. You can use hand soap or mild dishwashing liquid for cleaning dentures.
- When not wearing them, put dentures in a denture cleanser soaking solution or in water. Never put dentures in hot water, which can make them warp.
- If cared for properly, dentures should last a minimum of 5 years. Over time, the bone shrinks and causes the denture to become loose.
- An ill-fitting denture causes the bone to shrink more rapidly. To prolong the life of a denture, a dentist will often use a denture liner to refit the internal surface of the denture to the oral tissues.
- Minor fractures in the teeth or acrylic base can usually be repaired by a dental lab in 1 to 2 days.




DENTAL VENEERS
Dental veneers (sometimes called porcelain veneers or dental porcelain laminates) are wafer-thin, custom-made shells of tooth-coloured materials designed to cover the front surface of teeth to improve your appearance. These shells are bonded to the front of the teeth changing their colour, shape, size, or length.
Types:
- Porcelain veneers
- Resin Composite veneers
Indications:
- Teeth that are discoloured because of
- Root canal treatment
- Stains from Tetracycline and other drugs
- Excessive fluoride
- Large resin stains
- Other causes
- Worn out teeth
- Chipped off and broken teeth
- Misaligned, uneven, or irregularly shaped teeth
- Teeth with gaps between them
Advantages:
- They provide natural gum appearance.
- Porcelain veneers are stain resistant.
- They generally don’t require as much shaping as crowns do, yet they are much stronger and look better.
- A colour may be selected to make darker tooth appear white.
Risks:
- Usually cannot be repaired if chipped off or broken.
- Because enamel is removed, tooth may become sensitive to hot and cold food and drinks.
- Veneers may not exactly match the colour of your other teeth. Also, the veneer’s colour cannot be altered once it’s in place. If you plan on whitening your teeth, you need to do so before getting veneers.
- Though not likely, veneers can dislodge and fall off. To minimize the chance of this occurring, do not bite your nails, chew on pencils, ice or other hard objects, or otherwise put too much pressure on your teeth.
- People who clench and grind their teeth are poor candidates for porcelain veneers, as this can cause the veneers to crack or chip.
- Veneers are not a good choice for people with unhealthy teeth (for example, those with decay or active gum disease), weakened teeth (as a result of decay, fracture, large dental fillings), or for those who don’t have enough existing enamel on the tooth surface.
- Teeth with veneers can still experience decay, possibly necessitating full coverage of the tooth with a crown.
Procedure:
Dental veneers usually take 2-3 appointments.
1st appointment is for clinical check-up, diagnosis and discussing the treatment options with the patient.
2nd appointment: tooth preparation or cutting for the dental veneer is done. Numbing the area is decided by the dentist. Post preparation, impression is made and sent to the lab for fabrication of the veneers. Usually a temporary/ provisional veneers are given to protect the tooth and prevent sensitivity due to hot and cold food and drinks.
3rd appointment: cementation/fixation of the veneers are done with a special cement.
Lifespan: 7-15 years
Post treatment care:
- Maintaining good oral hygiene includingregular brushing, flossing and using a good antiseptic mouthwash.
- Avoid stain causing foods and beverages.




